The world of healthcare is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and one of the most significant developments is the rise of telemedicine. Telemedicine, often referred to as telehealth, offers innovative ways to deliver healthcare services, and it’s poised to play a pivotal role in diabetes care. In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits and challenges of telemedicine in managing diabetes, as well as its promising future.
The Benefits of Telemedicine in Diabetes Care
1. Improved Accessibility
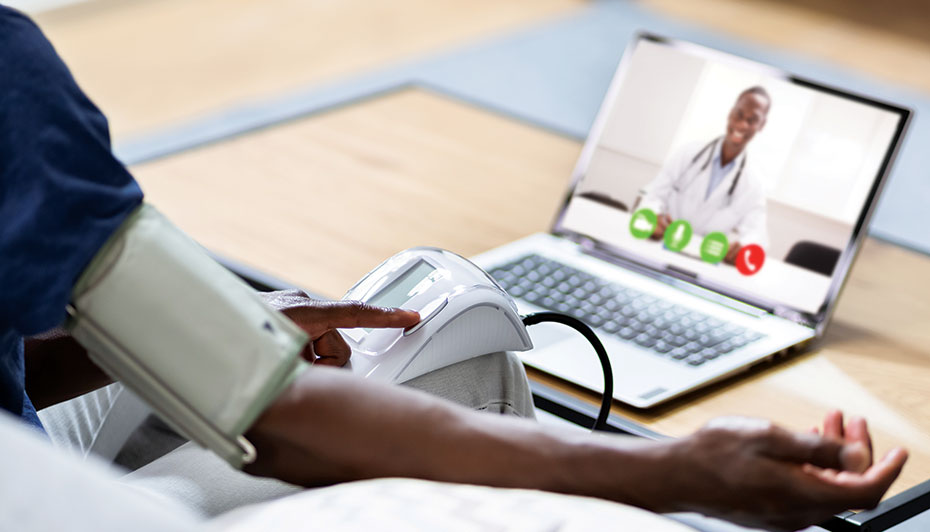
One of the primary advantages of telemedicine is improved accessibility. For individuals living with diabetes, especially in remote or underserved areas, accessing specialized care can be challenging. Telemedicine allows patients to consult with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes, reducing the barriers to regular care and support.
2. Convenience and Comfort
Telemedicine offers unparalleled convenience. Patients can schedule virtual appointments at times that suit their schedules, eliminating the need for travel and waiting rooms. This level of comfort promotes more frequent check-ins and enhances adherence to treatment plans.
3. Real-time Monitoring
With the help of wearable devices and smart sensors, telemedicine enables real-time monitoring of key metrics like blood glucose levels. Patients can transmit their data to healthcare providers who can then offer timely adjustments to their treatment plans. This real-time monitoring is invaluable in maintaining optimal diabetes control.
4. Personalized Care
Telemedicine facilitates a more personalized approach to diabetes care. Healthcare providers can engage in ongoing, one-on-one conversations with their patients, understand their unique needs, and tailor treatment plans accordingly. This approach empowers individuals to take charge of their health and improve their self-management skills.
The Challenges of Telemedicine in Diabetes Care
1. Technology Barriers
Not everyone has access to the necessary technology for telemedicine, such as smartphones or high-speed internet. This digital divide can limit the reach of telemedicine and exclude certain patient populations.
2. Privacy and Security
Patient data security is a significant concern in telemedicine. Healthcare providers must ensure that patient information is protected and complies with privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. Cybersecurity measures must be robust to safeguard sensitive health data.
3. Limited Physical Examinations
Some aspects of diabetes care, like physical examinations or blood tests, may be challenging to conduct remotely. Telemedicine can complement traditional in-person care, but not fully replace it. Finding the right balance is crucial.
4. Regulatory and Reimbursement Hurdles
Telemedicine is subject to varying regulations and reimbursement models across different regions and healthcare systems. Ensuring uniform access and reimbursement for telemedicine services remains an ongoing challenge.
The Future of Telemedicine in Diabetes Care
The future of telemedicine in diabetes care is undoubtedly promising. As technology continues to advance and healthcare systems adapt, telemedicine is set to become more integrated into diabetes management. With the potential for artificial intelligence, machine learning, and remote monitoring, telemedicine can offer even more precise and proactive care.
As the world grapples with an increasing burden of chronic conditions like diabetes, telemedicine is positioned to play a vital role in addressing the growing demand for healthcare services. Its benefits in terms of accessibility, convenience, real-time monitoring, and personalized care are clear. To overcome challenges related to technology, privacy, physical examinations, and regulations, collaboration among healthcare providers, tech companies, and policymakers is essential.
In summary, the future of telemedicine in diabetes care is bright. It holds the potential to revolutionize the way individuals manage their diabetes, offering a more patient-centric, convenient, and effective approach to care. With ongoing innovation and concerted efforts to address the associated challenges, telemedicine is set to play a significant role in improving diabetes management and overall healthcare delivery.
IoT Technology Revolutionizing Diabetes Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the landscape of healthcare, and one area where its impact is particularly noteworthy is diabetes management. IoT technology is revolutionizing the way individuals monitor, track, and control their diabetes. In this mini-blog, we’ll explore how IoT is changing the game in diabetes care.
Real-time Data and Remote Monitoring
One of the key advantages of IoT in diabetes management is the ability to collect real-time data from various devices and sensors. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, and wearable sensors can transmit vital information to healthcare providers and patients instantly. This data is invaluable in maintaining optimal blood sugar control.
Personalized Treatment Plans
IoT technology enables healthcare providers to offer highly personalized treatment plans based on individual data. With access to real-time information, doctors can make timely adjustments to medication and lifestyle recommendations, ensuring that patients receive tailored care that maximizes the effectiveness of their diabetes management.
Enhanced Self-Management
For individuals with diabetes, IoT empowers them to take control of their health. Through smartphone apps and wearable devices, they can track their blood glucose levels, monitor their diet and exercise, and receive instant feedback and alerts. This level of self-management not only improves overall health but also increases patient engagement and adherence to their treatment plans.
Remote Consultations
Telemedicine is on the rise, and IoT plays a crucial role in enabling remote consultations for diabetes management. Patients can connect with their healthcare providers via video calls, sharing their real-time data and discussing their progress without the need for in-person visits. This convenience enhances access to care, especially for those in remote or underserved areas.
Predictive Insights
IoT technology can leverage predictive analytics to anticipate blood sugar fluctuations and other diabetes-related events. By analyzing historical data and individual patterns, IoT devices can provide early warnings, helping patients take preventive actions to avoid dangerous highs and lows.
Challenges and Privacy Concerns
While IoT technology offers tremendous benefits, it also comes with challenges and privacy concerns. Ensuring the security of patient data is paramount, as is addressing issues related to data accuracy, device interoperability, and regulatory compliance.
In conclusion, IoT technology is changing the game in diabetes management by providing real-time data, personalized treatment plans, enhanced self-management, remote consultations, and predictive insights. The future of diabetes care is becoming more patient-centric, convenient, and effective, thanks to IoT. As technology continues to advance and healthcare systems adapt, we can expect even more significant innovations in diabetes management, ultimately improving the lives of individuals with diabetes.